(Solved) : Using Algorithm Depth First Traversal Left Complete Exercises 3 5 Right Instead Implement Q37227566 . . .

Using the algorithm for depth first traversal (left), completeexercises 3 and 5 (right). Instead of implementing the algorithm,write the code in Java and test the code using the graphs inexercise 1.
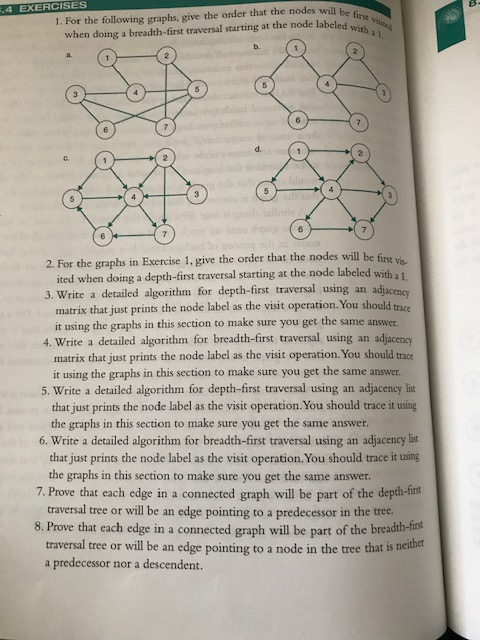
end. We then continue to back up until because all nodes adjacent to it have been list of nodes in the order visited is [1,2, 3,4 The recursive algorithm for depth-first DepthFirstTraversal (G, v) // G is the graph // v is the current node Visit( v) Mark( v) for every edge vw in G do if w is not marked then DepthFirstTraversal (G, w) end if end for This recursive algorithm relies on the track of where it has been in the graph reaches dead ends. We could create a sin stack data structure and pushing and po 8.3.2 Breadth-First Trave will be first labeled with a 1 4 EXERCISES 1. For the following graphs, give the order that the nodes when doing a breadth-first traversal starting at the node labeled with b. 2. For the graphs in Exercise 1. give the order that the nodes will be fins a 1, ited when doing a depth-first traversal starting at the node labeled with first traversal using an adjacency 3. Write a detailed algorithm for depth- matrix that just prints the node label as the visit operation. You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer 4. Write a detailed algorithm for breadth-first traversal using an adjacency matrix that just prints the node label as the visit operation. You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer. 5. Write a detailed algorithm for depth-first traversal using an adjacency lis that just prints the node label as the visit operation.You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer. 6. Write a deailed algorithm for breadth-first traversal using an adjacency ist that just prints the node label as the visit operation. You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer. 7. Prove that each edge in a connected graph will be part of the depth-firt traversal tree or will be an edge pointing to a predecessor in the tree. 8. Prove that each edge in a connected graph will be part of the breadth-hi traversal tree or will be an edge pointing to a node in the tree that is netn a predecessor nor a descendent. Show transcribed image text end. We then continue to back up until because all nodes adjacent to it have been list of nodes in the order visited is [1,2, 3,4 The recursive algorithm for depth-first DepthFirstTraversal (G, v) // G is the graph // v is the current node Visit( v) Mark( v) for every edge vw in G do if w is not marked then DepthFirstTraversal (G, w) end if end for This recursive algorithm relies on the track of where it has been in the graph reaches dead ends. We could create a sin stack data structure and pushing and po 8.3.2 Breadth-First Trave
will be first labeled with a 1 4 EXERCISES 1. For the following graphs, give the order that the nodes when doing a breadth-first traversal starting at the node labeled with b. 2. For the graphs in Exercise 1. give the order that the nodes will be fins a 1, ited when doing a depth-first traversal starting at the node labeled with first traversal using an adjacency 3. Write a detailed algorithm for depth- matrix that just prints the node label as the visit operation. You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer 4. Write a detailed algorithm for breadth-first traversal using an adjacency matrix that just prints the node label as the visit operation. You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer. 5. Write a detailed algorithm for depth-first traversal using an adjacency lis that just prints the node label as the visit operation.You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer. 6. Write a deailed algorithm for breadth-first traversal using an adjacency ist that just prints the node label as the visit operation. You should trace it using the graphs in this section to make sure you get the same answer. 7. Prove that each edge in a connected graph will be part of the depth-firt traversal tree or will be an edge pointing to a predecessor in the tree. 8. Prove that each edge in a connected graph will be part of the breadth-hi traversal tree or will be an edge pointing to a node in the tree that is netn a predecessor nor a descendent.
Expert Answer
Answer to Using the algorithm for depth first traversal (left), complete exercises 3 and 5 (right). Instead of implementing the al…
OR