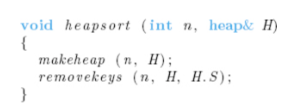Implement The Linear-Time Makeheap Algorithm: Read In N Unsorted Numbers And Create A Heap (Stored As An Array) To Store These N Number. Est This Program With Input Of N=100 Numbers And Print Out The Heap Structure By Depth. For Example, Or The Heap Shown On The Right, The Print Result Is: D=0:30d=1:25,20d=2:18,12,19,17d=3:16,14,11 2. Implement The
Follow the prompt exactly and do it in java please using the pseudocode: Implement The Linear-Time Makeheap Algorithm: Read In N Unsorted Numbers And Create A Heap (Stored As An Array) To Store These N Number. Est This Program With Input Of N=100 Numbers And Print Out The Heap Structure By Depth. For Example, Or The Heap Shown On The Right, The Print Result Is: D=0:30d=1:25,20d=2:18,12,19,17d=3:16,14,11 2. Implement The

Expert Answer
1
public class MakeHeap {
public static void makeHeap(int[] arr, int n) {
// Build the heap bottom-up by calling trickleDown for each non-leaf node
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
trickleDown(arr, n, i);
}
}
public static void trickleDown(int[] arr, int n, int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest]) {
largest = left;
}
if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest]) {
largest = right;
}
if (largest != i) {
// Swap arr[i] and arr[largest]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = temp;
// Recursively trickle down the affected subtree
trickleDown(arr, n, largest);
}
}
public static void printHeapByDepth(int[] arr, int n) {
int depth = 0;
int currentIndex = 0;
int currentDepthSize = 1;
while (currentIndex < n) {
System.out.print("d=" + depth + ": ");
for (int i = currentIndex; i < Math.min(currentIndex + currentDepthSize, n); i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
currentIndex += currentDepthSize;
currentDepthSize *= 2;
depth++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 100;
int[] arr = new int[n];
// Initialize arr with your input of 100 numbers
// For example:
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 1000); // Replace with your input method
}
// Create a heap from the array
makeHeap(arr, n);
// Print the heap structure by depth
printHeapByDepth(arr, n);
}
}
The Java code I provided follows the pseudocode for creating a heap and printing the heap structure…
OR