(Solved) : 2 Nearest Neighbor Number Cities Arranged Graph Divided Like Ordinary Cartesian Plane City Q44051613 . . .
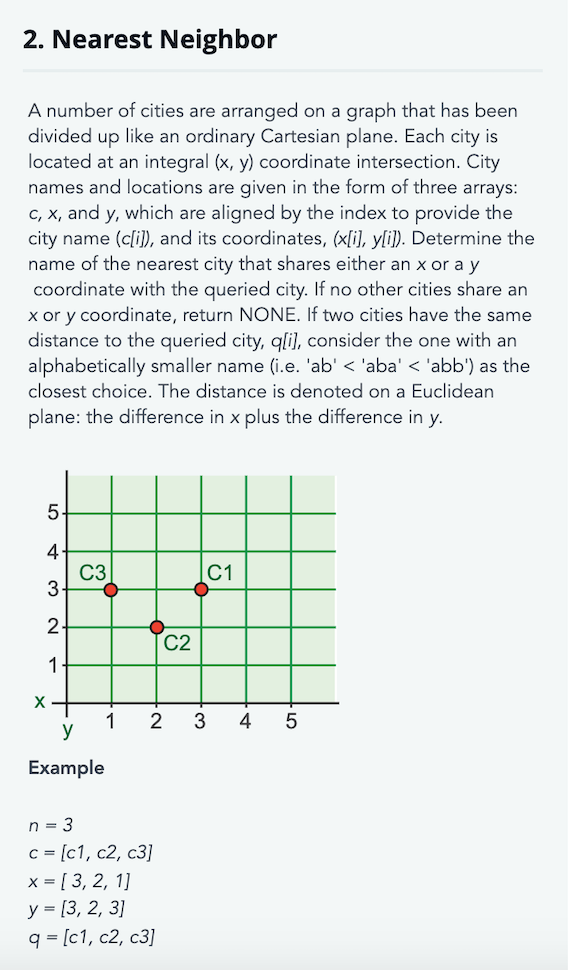
![The three points at (x[i], y[i]) are (3,3), (2,2) and (1,3) represent the coordinates of the cities on the graph. The nearest](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/f34/f346c1e3-8dcb-4461-b4e0-f064a3ca88a8/phpzy9FXA.png)

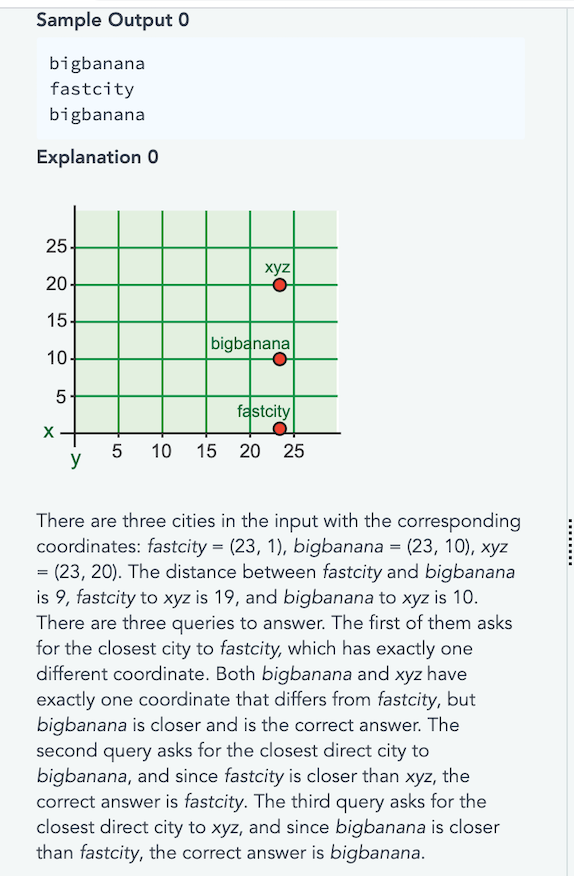
![Sample Case 1 Sample Input 1 STDIN Function ----- - - - - - - - - c[] size n = 3 c = [london, warsaw, hacker 3 → london](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/9db/9db282f5-38db-4349-8307-d5a73dcd2efd/phpWKUX9B.png)

![y[] size n = 5 y[] = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500] + en q[] size m = 5 9[] = [green, red, blue, yel low Sample Output 2 NO](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/c1e/c1e918fb-79db-49ad-8228-ed419f5c448c/phpGbZHmh.png)
Please help with your Java Solution
2. Nearest Neighbor A number of cities are arranged on a graph that has been divided up like an ordinary Cartesian plane. Each city is located at an integral (x, y) coordinate intersection. City names and locations are given in the form of three arrays: c, x, and y, which are aligned by the index to provide the city name (c[i]), and its coordinates, (x[i], y[i]). Determine the name of the nearest city that shares either an x or a y coordinate with the queried city. If no other cities share an x or y coordinate, return NONE. If two cities have the same distance to the queried city, q[i], consider the one with an alphabetically smaller name (ie. ‘ab'<‘aba’ < ‘abb’) as the closest choice. The distance is denoted on a Euclidean plane: the difference in x plus the difference in y. in c3_ 01 ñ ñ -J- i 2 3 4 5 Example n = 3 C = [c1, c2, c3] x = [3, 2, 1) y = 13, 2, 3] q = [c1, c2, c3] The three points at (x[i], y[i]) are (3,3), (2,2) and (1,3) represent the coordinates of the cities on the graph. The nearest city to c1 is c3, which shares a y value (distance = (3-1) + (3-3) = 2). City c2 does not have a nearest city as none share an x or y with c2, so this query returns NONE. A query of c3 returns c1 based on the first calculation. The return array after all queries are complete is (c3, NONE, c1]. Function Description Complete the function closestStraightCity in the editor below. The function must return an array of m strings, where the index of i element of this array denotes the return value of the index of i query. closestStraightCity has the following parameter(s): string [] c: an array of strings that represent the names of each city[i] int[] x: an array of integers, the x coordinates of each city[i] int[] y: an array of integers, the y coordinates of each city[i] stringll q: an array of strings, two dash-separated integers representing a query location Constraints • 1 sn, m s 105 • 1 s x[i].y[i] s 109 • 1 s length of q[i] and c[i] = 10 • Each character of all c[i] and q[i] is in the range ascii[a-z, 0- 9,-) • All city name values, c[i], are unique • All cities have unique coordinates Input Format For Custom Testing In the first line, there is a single integer n, the size of the carray. Each of the next n lines contains a string c[i]. In the next line, the integer n repeats, the size of the x array. Each of the next n lines contains an integer, x[i]. The next line, the integer n repeats, the size of the y array. Each of the next n lines contains an integer, yli). The next line contains an integer, m, the size of q. Each of the next m lines contains a string, q[j] Sample Case 0 Sample Input 0 STDIN Function Pai + c[] Size n : C[] = [“fast + 3 fastcity bigbanana xyz + x[] Size n : x[] = [23, : + y[] Size n : y[] = [1, 11 q[] Size m : 9[] = [“fast fastcity bigbanana xyz Sample Output 0 bigbanana fastcity bigbanana Explanation 0 bigbanana fastcity V 5 10 15 20 25 There are three cities in the input with the corresponding coordinates: fastcity = (23, 1), bigbanana = (23, 10), xyz = (23, 20). The distance between fastcity and bigbanana is 9, fastcity to xyz is 19, and bigbanana to xyz is 10. There are three queries to answer. The first of them asks for the closest city to fastcity, which has exactly one different coordinate. Both bigbanana and xyz have exactly one coordinate that differs from fastcity, but bigbanana is closer and is the correct answer. The second query asks for the closest direct city to bigbanana, and since fastcity is closer than xyz, the correct answer is fastcity. The third query asks for the closest direct city to xyz, and since bigbanana is closer than fastcity, the correct answer is bigbanana. Sample Case 1 Sample Input 1 STDIN Function —– – – – – – – – – c[] size n = 3 c = [“london”, “warsaw”, “hacker 3 → london warsaw hackerland x[] size n = 3 x = [1, 10, 20] → 3 1 + y[] size n = 3 y = [1, 10, 10] [] size m = 3 q = [“london”, “warsaw”, “hacker → london − warsaw hackerland Sample Output 1 NONE hackerland warsaw Explanation 1 warsaw hackerland london y 5 10 15 20 25 Explanation 1 157 warsaw hackerland 10+ london X 9 5 10 15 20 25 The cities are located as follows: london = (1, 1), warsaw = (10, 10), and hackerland = (20,10). There are no other cities on a row or column shared with london, so the first query returns NONE. The cities of warsaw and hackerland share y values, so they are the closest to each other. Sample Case 2 Sample Input 2 IN Function en c[] size n = 5 c[] = [“green”, “red”, “blue”, “yel low к x[] size n = 5 x[] = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500] → → [] size n = 5 y[] = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500] y[] size n = 5 y[] = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500] + en q[] size m = 5 9[] = [“green”, “red”, “blue”, “yel low Sample Output 2 NONE NONE NONE NONE NONE Explanation 2 pink | I pink yellow blue Tred green y 100 200 300 400 500 None of the cities share a row or a column, so none meet the criteria for being considered closest. Show transcribed image text 2. Nearest Neighbor A number of cities are arranged on a graph that has been divided up like an ordinary Cartesian plane. Each city is located at an integral (x, y) coordinate intersection. City names and locations are given in the form of three arrays: c, x, and y, which are aligned by the index to provide the city name (c[i]), and its coordinates, (x[i], y[i]). Determine the name of the nearest city that shares either an x or a y coordinate with the queried city. If no other cities share an x or y coordinate, return NONE. If two cities have the same distance to the queried city, q[i], consider the one with an alphabetically smaller name (ie. ‘ab’
Expert Answer
Answer to 2. Nearest Neighbor A number of cities are arranged on a graph that has been divided up like an ordinary Cartesian plane…
OR