(Solved) : 53 Matlab Exercises 1 Extend Factorial Function Defined Checks Positive Input Argument 2 W Q35182412 . . .
5.3) MATLAB Exercises
1. Extend the factorial function defined above, such that it checksfor a positive input argument.
2. Write a function that calculates a random walk trajectory basedon the iteration xi+1 = xi + , where
is a uniformlydistributed random variable between -1 and 1. Plot the resultingtrajectory.
3. Change the sorting algorithm given below such that itsorts the elements in descending order. Compare the speed of yourfunction with the built-in MATLAB function sort.
4. Approximation of π. The area of a circle is given byA = πr^2 where r is the radius. Assume a circle with r = 0.5embedded in a unit square. A point in the unit square is defined byp = (x,y) where 0 ≤ x,y ≤ 1. If we draw ntot times two uniformlydistributed random numbers (x,y) and count how often thecorresponding points falls into the circle (ncirc), we get anapproximation of the circle area by ncirc /ntot and by that of thenumber π. Write a function which approximates π by the describedmethod. How many draws do you need to get the rst three digitsright?
Note: part 3 to 4 missing (Please answer the tworemaining parts). I forgot to put oninstructions on part 2 maybe that changes everything. For somereason the symbol didn’t transfer over here on text but I manage tofixed now. I manage to add the sorting algorithm example in part 3below but it needs to be change in descending order and compare thespeed of your function with the built-in MATLAB functionsort..
My answer part 1)
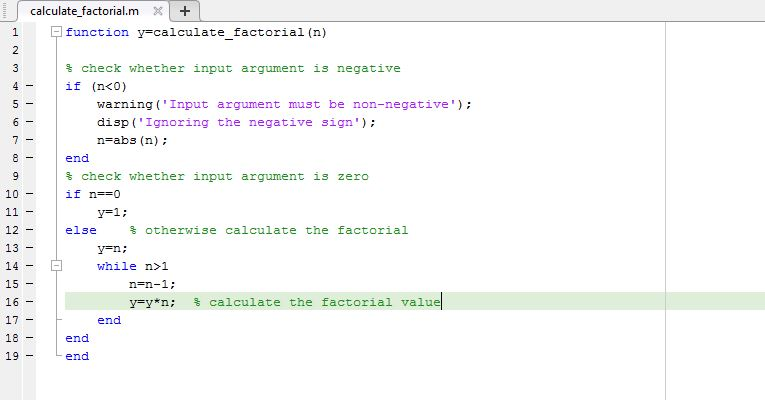
function y=calculate_factorial(n)
% check whether input argument is negative
if (n<0)
warning(‘Input argument must be non-negative’);
disp(‘Ignoring the negative sign’);
n=abs(n);
end
% check whether input argument is zero
if n==0
y=1;
else % otherwise calculate the factorial
y=n;
while n>1
n=n-1;
y=y*n; % calculate the factorial value
end
end
end
SCREENSHOT OF CODE:
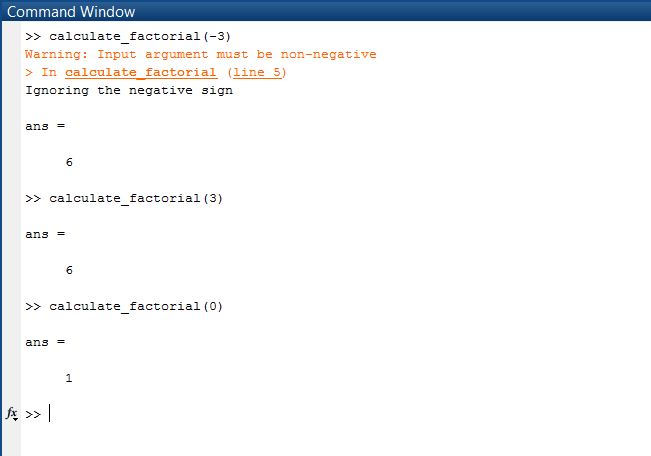
SAMPLE OUTPUT:
part 2)
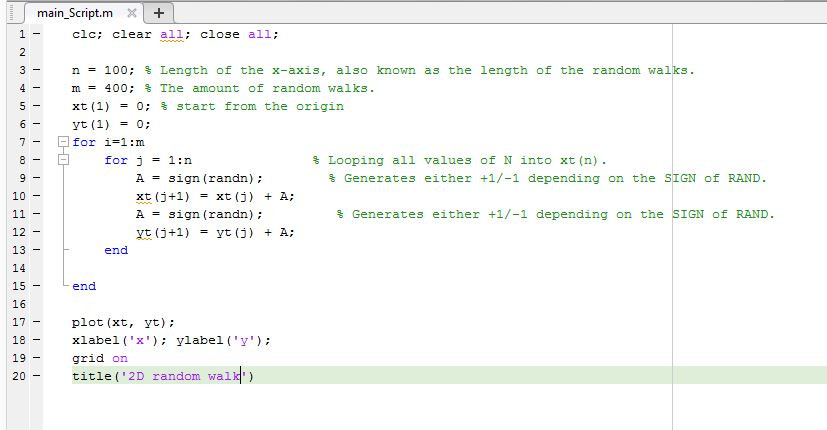
clc; clear all; close all;
n = 100; % Length of the x-axis, also known as the length of therandom walks.
m = 400; % The amount of random walks.
xt(1) = 0; % start from the origin
yt(1) = 0;
for i=1:m
for j = 1:n % Looping all values of N into xt(n).
A = sign(randn); % Generates either +1/-1 depending on the SIGN ofRAND.
xt(j+1) = xt(j) + A;
A = sign(randn); % Generates either +1/-1 depending on the SIGN ofRAND.
yt(j+1) = yt(j) + A;
end
end
plot(xt, yt);
xlabel(‘x’); ylabel(‘y’);
grid on
title(‘2D random walk’)
=============================== SCREENSHOT OF CODE
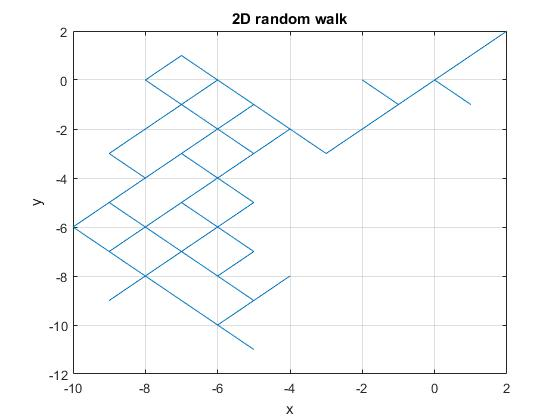
============================================ SAMPLE OUTPUT
Example for part 3 needs to be change in descendingorder the example below is in ascending order: thefollowing function sorts the elements of a vector in ascendingorder.
function v = gsort(v)
pos = 2;
while pos <= length(v) if v(pos)>v(pos-1) % move to thenext position
pos = pos + 1;
else % swap the values
foo = v(pos-1);
v(pos-1) = v(pos);
v(pos) = foo;
if pos > 2 % decrease position
pos = pos – 1;
end
end
end
We were unable to transcribe this imageWe were unable to transcribe this imageWe were unable to transcribe this imagecalculate factorial.m+ function y=calculate factorial (n) check whether input argument 13 negative warning (‘Input argument must be non-negative’): disp’Ignoring the negative sign) n=abs (n) ; end % check whether input argument is zero if n 0 10 Y-1: 12else 13 % otherwise calculate the factorial y=n; while 15 16 n>1 n-n-1: y=y*n; % calculate the factorial value end end end Command Window > calculate factorial (-3) Warning: Input argument must be non-negative > In calculate factorial (line 5) Ignoring the negative sign ans – >> calculate_factorial (3) ans – >> calculate_factorial (0) ans – fx >> main_Script.m+ clc: clear all: close all: n = 100; % Length of the x-axis, also known as the length of the random walks. m 400; % The amount of random walks. xt (1) % start from the origin yt (1) = 0; for i-1:m 4- for 1 : n % Looping all values of N into xt (n) . % Generates either +1/-1 depending on the SIGN of RAND A 3ign (randn) ; xt(j+1) = xt (j) + A; A = 3ign (randn) ; 10 % Generates either +1/-1 depending on the SIGN of RAND 12 13 14 end end 16 17 plot (xt, yt); x1abe1 ( ·x’ ) ; ylabel ( ‘y’) ; grid on title (‘2D random wall) 20 2D random walk 2 -2 -4 -6 -8 -10 -12 -6 -2 2 -10 -8 Show transcribed image text
Expert Answer
Answer to 53 Matlab Exercises 1 Extend Factorial Function Defined Checks Positive Input Argument 2 W Q35182412 . . .
OR